

No products in the cart.


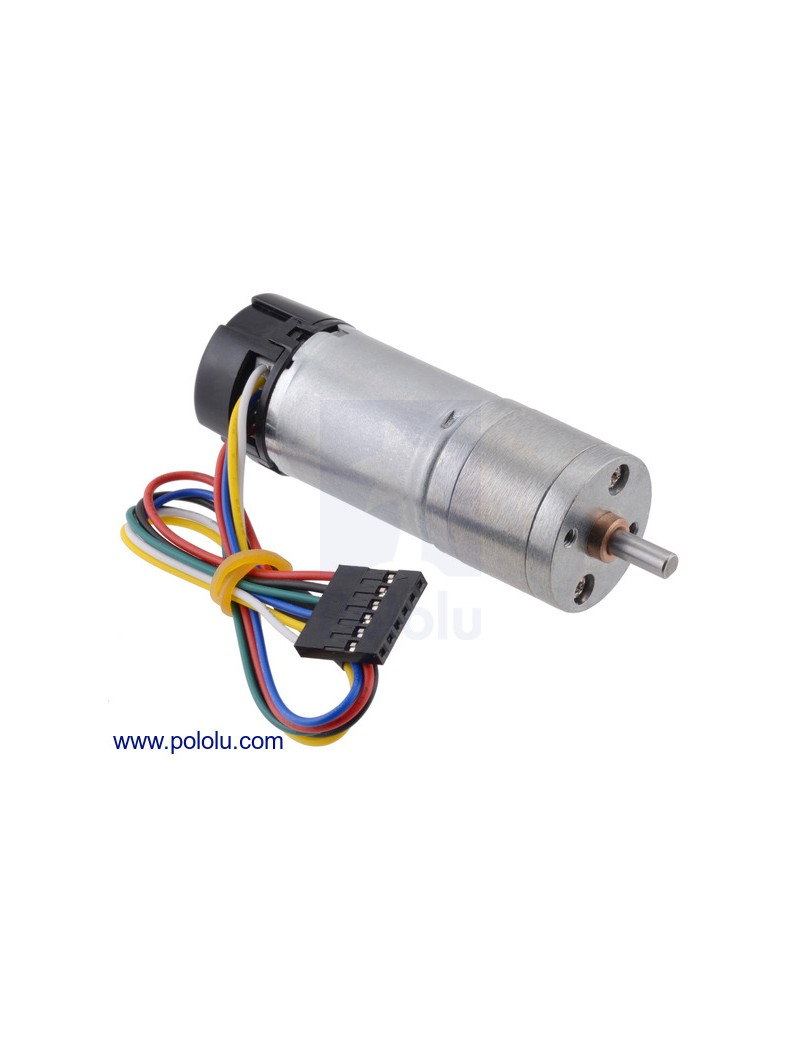
This gearmotor consists of a high-power, 12 V brushed DC motor combined with a 98.78:1 metal spur gearbox, and it has an integrated 48 CPR quadrature encoder on the motor shaft, which provides 4741.44 counts per revolution of the gearbox’s output shaft. The gearmotor is cylindrical, with a diameter just under 25 mm, and the D-shaped output shaft is 4 mm in diameter and extends 12.5 mm from the face plate of the gearbox. This gearmotor is also available without an encoder.
Key specifications:
| voltage | no-load performance | stall extrapolation |
|---|---|---|
| 12 V | 100 RPM, 300 mA |
29 kg⋅cm (400 oz⋅in), 5.0 A |
These cylindrical brushed DC gearmotors are available in a wide range of gear ratios and with five different motors (two power levels of 6 V motors and three power levels of 12 V motors). The gearmotors all have the same 25 mm diameter case and 4 mm diameter gearbox output shaft, so it is generally easy to swap one version for another if your design requirements change (though the length of the gearbox tends to increase with the gear ratio). The motor and encoder portion is available by itself (no gearbox) for each combination of power level and nominal operating voltage, and versions without the encoder are also available. See the 25D metal gearmotor datasheet (2MB pdf) for more information, including detailed performance graphs for each gearmotor version. You can also use our dynamically sortable 25D gearmotor comparison table to search for the version that offers the best combination of speed, torque, and current draw for your particular application. A more basic comparison table is available below.
Exact gear ratio: 22×22×22×22×22×2312×10×10×10×10×10≈98.78:122×22×22×22×22×2312×10×10×10×10×10≈98.78:1
The diagram below shows the dimensions of the 25D mm line of gearmotors (units are mm over [inches]). This diagram is also available as a downloadable PDF (171k pdf).
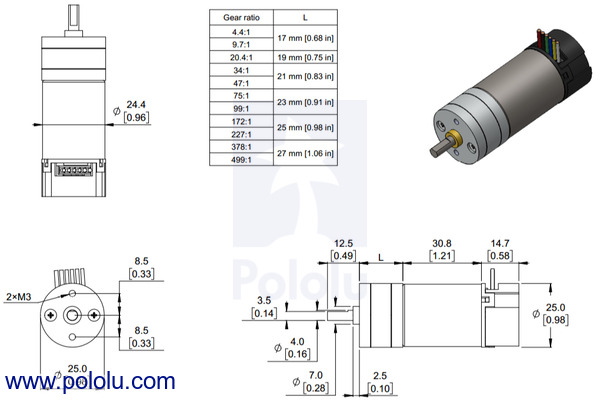 |
A two-channel Hall effect encoder is used to sense the rotation of a magnetic disk on a rear protrusion of the motor shaft. The quadrature encoder provides a resolution of 48 counts per revolution of the motor shaft when counting both edges of both channels. To compute the counts per revolution of the gearbox output, multiply the gear ratio by 48. The motor/encoder has six color-coded, 8″ (20 cm) leads terminated by a 1×6 female header with a 0.1″ pitch, as shown in the main product picture. This header works with standard 0.1″ male headers and our male jumper and precrimped wires. If this header is not convenient for your application, you can pull the crimped wires out of the header or cut the header off. The following table describes the wire functions:
| Color | Function |
|---|---|
| Red | motor power (connects to one motor terminal) |
| Black | motor power (connects to the other motor terminal) |
| Green | encoder GND |
| Blue | encoder Vcc (3.5 V to 20 V) |
| Yellow | encoder A output |
| White | encoder B output |
| Size: | 25D x 69L mm1 |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 104 g |
| Shaft diameter: | 4 mm2 |
| Gear ratio: | 98.78:1 |
|---|---|
| No-load speed @ 12V: | 100 rpm3 |
| No-load current @ 12V: | 0.30 A4 |
| Stall current @ 12V: | 5.0 A5 |
| Stall torque @ 12V: | 29 kg·cm5 |
| No-load speed @ 6V: | 50 rpm6 |
| Stall current @ 6V: | 2.5 A6 |
| Stall torque @ 6V: | 15 kg·cm6 |
| Motor type: | 12V, 5.0A stall (HP 12V) |
| Max efficiency @ 12V: | 36 % |
|---|---|
| Speed at max efficiency: | 87 rpm |
| Torque at max efficiency: | 4.5 kg·cm |
| Current at max efficiency: | 0.94 A |
| Output power at max efficiency: | 4.0 W |
| Lead length: | 8 in7 |
|---|---|
| Encoders?: | Y |